09 Jun Vitamin D – The Sunshine Vitamin
Vitamin D is arguably the single most underrated nutrient, likely because, it’s Free.
Your body naturally makes Vitamin D when sunlight touches your skin.
It is nearly impossible to get adequate amounts of Vitamin D solely through your diet. There are fortified vitamin D foods such as milk and cereals available, most provide vitamin D2, a form which is much less well utilized by the body than D3.
Good dietary sources include:
-
Fortified foods (milk, cereals, orange juice)
-
Eggs (yolk)
-
Salmon
-
Tuna
-
Mackerel
-
Sardines
You would have to drink 10 tall glasses of vitamin D fortified milk each day just to get a minimum levels of Vitamin D into your diet …
Your body CAN’T make other vitamins, and need to get these from the foods you eat. For example, Vitamin C is abundant in fruits and vegetables.
Your body CAN make Vitamin D when your skin is exposed to sunlight. Unlike other vitamins, when your body gets vitamin D it turns it into a hormone called “activated vitamin D”, or calcitriol.
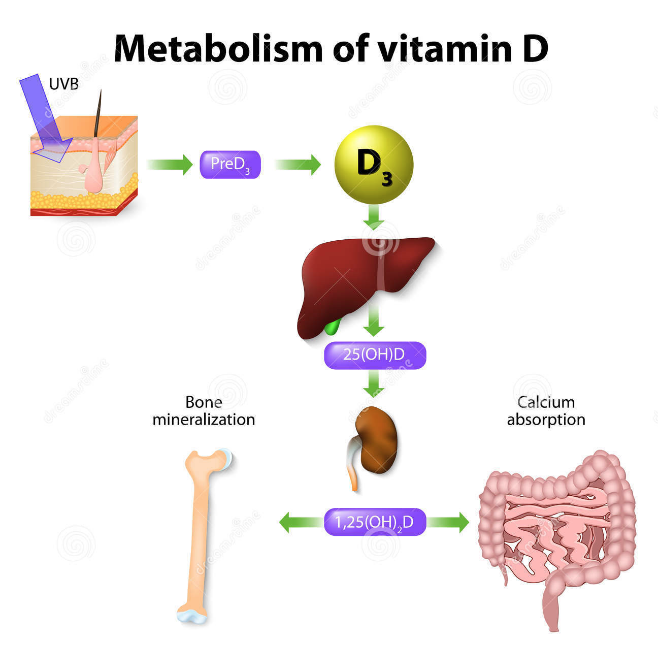
You need Vitamin D to absorb calcium and phosphorus to develop structure and strength of bones. When your skin is exposed to the sun, it produces vitamin D and sends it to your liver. If you take a supplement or eat foods with Vitamin D your gut sends Vitamin D to your liver. The liver changes it to a substance called 25(OH)D that is sent all over the body through the bloodstream. When you get your Vitamin D levels tested, 25(OH)D is what they are measuring in your blood.
From here your kidneys turn 25(OH)D into activated Vitamin D, now ready to perform.
Once activated, Vitamin D:
-
Manages calcium in your blood, bones and gut
-
Helps cells all over your body to communicate properly
-
Vitamin D may prevent osteoporosis, depression, prostate and breast cancer, and even effects diabetes and obesity.
The therapeutic rays of natural sunlight that generate Vitamin D in your skin cannot penetrate glass. So you don’t generate Vitamin D when sitting in your car or home. Your skin must also be free of sunscreen, sun blocks and clothing, which all interfere with the process.
How Much Vitamin D do I need?
The Institute of Medicine (IOM) recomneds:
-
Men & Women < age 50: 400-800 IU/day
-
Age 50 and older: 800-1000 IU/day
On days when you can’t get enough sun exposure, taking a supplement is an effective way to get what your body needs.
Supplements, what form and how much?
The Vitamin D Council recommends taking vitamin D3 rather than vitamin D2. Vitamin D3 is what your body produces in response to sun exposure. In the US, most over-the-counter vitamin D supplements are D3.
Vitamin D supplements can be taken with or without food and the full amount can be taken at one time.
If you have kidney disease or liver damage this can impair your body’s ability to activate circulating Vit D. Always check with your doctor first before supplementing if you have other medical concerns and taking other medications.
Can I take too much Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat soluble Vitamin, meaning your body has a harder time getting rid of it vs a water soluble vitamin. In perspective, your body can produce 10,000-25,000 IUs of vitamin D after a little bit of full body sun exposure. Vitamin D toxicity could happen if you take 40,000 IU a day for a couple of months or longer.
What about skin cancer?
Exposing your skin to the sun for too long, so that your skin starts to burn can be dangerous, increasing your risk for developing skin cancer. Research shows that moderate but frequent sun exposure is healthy, but overexposure and intense exposure can increase your risk of skin cancer (just like everything else… moderation!).
You want to expose your skin for half the time it takes for you to begin to burn. This varies based on how dark or light your skin color. For example, if you have lighter skin (less melatonin) it might take around 15 minutes of sun exposure to get the vitamin D you need, while if you have darker skin (more melatonin) it might take six times longer (up to 2 hours). After you get the exposure you need, cover up with clothing and go into the shade. Or use a sunscreen that blocks both UVA light and UVB light.
Go out for a 15 minute walk with your legs and arms exposed or enjoy your lunch outside today!